Explore the rich and fascinating history of astrology in this brief historical overview. From its ancient origins to its modern-day practice, discover how astrology has evolved across time and how it has impacted cultures worldwide.
This post may contain affiliate links and I may earn a small commission when you click on the links at no additional cost to you! Thank you in advance for helping to support the site!
What is Astrology?
Chances are, you already know a bit about astrology! Are you a Libra like me? Maybe a Pisces or a Sagittarius? Maybe you’ve looked up your horoscope in a magazine or on an app. All of these are determined using Astrology!
So your zodiac sign? That’s your sun sign! But your actual birth chart is full of complex placements that show the full picture of your personality. Those horoscopes that tell you how your day or week might go are based on the astrology for the day, and how they might relate to you based on your own signs!
Astrology has been practiced by humans for thousands of years. It is a system of belief that suggests that the positions and movements of celestial bodies, such as the sun, moon, planets, and stars, have a direct influence on human affairs and terrestrial events. Let’s explore the history of astrology, tracing its evolution from its earliest origins to its present-day practice.
Astrology is a field of study that uses the positions and movements of celestial bodies, such as stars and planets, to understand and interpret human affairs and natural phenomena. The basic premise of astrology is that the positions of these celestial bodies at the time of a person’s birth can influence their personality traits, relationships, and even their destiny.

Origins of Astrology
The origins of astrology are somewhat shrouded in mystery, but it’s believed that the practice emerged independently in different parts of the world around the same time, with various cultures developing their own unique systems and methods. However, it’s widely accepted that astrology began to spread and gain popularity in the ancient Near East, particularly in Babylon, where astrologers were highly respected and played a crucial role in political and religious affairs. The knowledge and practice of astrology then spread to other civilizations in the region, such as Egypt and Greece, where it was further developed and refined.
The Babylonians were particularly skilled at observing the heavens and recording the movements of celestial bodies, they believed that these movements could be used to predict events on Earth. This led to the development of many of the basic principles of astrology that are still used today such as the zodiac: a system of twelve constellations that are used to represent the positions of the planets and stars. The concept of planetary hours, which divides the day and night into twelve equal parts, each of which is associated with a particular planet, was also created by these early Astrologers.
The Greeks built upon the work of the Babylonians, adding their own insights and ideas to the field of astrology. The most famous Greek astrologer was Ptolemy, who lived in the second century AD. He wrote a book called the Tetrabiblos (tetra·bib·los), which is still studied today. In this book, he outlined the principles of astrology and how it could be used to predict events. The Greeks also developed the concept of the natal chart, which is a chart that shows the positions of the planets and stars at the moment of a person’s birth. This horoscope is used to give insights into a person’s personality and future events. The astrolabe is an ancient astronomical instrument used for solving problems related to time and the position of the stars. Its exact origins are not entirely clear, but it is believed to have been invented by the ancient Greeks, possibly around the 2nd century BCE. The first written mention of the astrolabe dates back to the 3rd century BCE, in the work of Greek mathematician and astronomer Hipparchus.
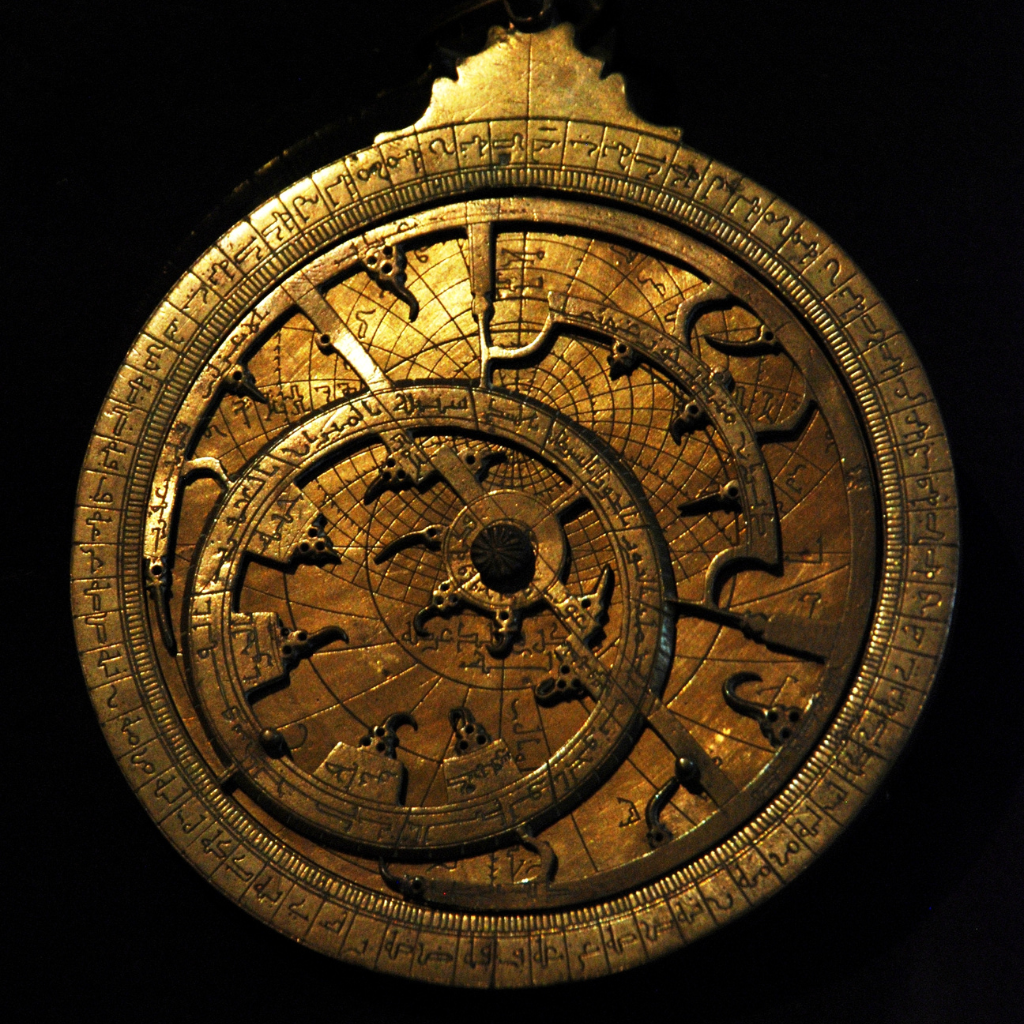

An astrolabe consists of a circular disk with a rotating arm that has marked degrees, angles, and celestial bodies engraved on it. It was used to determine the positions of stars and planets, the time of day or night, and the altitude and azimuth of celestial bodies. It works based on the principles of triangulation and can be used to find the position of celestial bodies in the sky relative to the observer’s location.
One of the earliest civilizations to use astrology was ancient Egypt. The Egyptians believed that the movements of the stars and planets had a direct influence on the lives of individuals and society as a whole. They used astrology to help them make important decisions, such as when to plant crops or build temples. The ancient Egyptians made a significant contribution to astrology with the development of the Sothic calendar, that was based on the movements of the stars. This calendar was an important tool for astrologers in predicting celestial events and understanding the influence of the stars on human affairs. The calendar centered around the observation of the star Sirius, which was believed to be a symbol of rebirth and renewal.
The Egyptians also developed a complex system of astrology that was based on the placement of the planets in the sky at the time of a person’s birth; believing that the position of the planets at the time of birth could provide insight into a person’s character and destiny. There is not a specific name for their system of astrology however, their astrological system is often referred to as Egyptian astrology or Egyptian star-lore.

Astrology in the Middle Ages
Throughout the centuries, astrology continued to spread and evolve, with practitioners adapting and integrating new concepts and techniques as they encountered them. In the Middle Ages, for instance, Islamic scholars made significant contributions to the field, particularly in the areas of astrology and astronomy. Eventually, astrology made its way to Europe, where it became especially popular during the Renaissance, it was believed that the positions of the planets and stars could have a direct impact on the fate of individuals and nations; leading royalty and nobility to frequently hire consulting Astrologers to help them make important decisions.
Islamic Golden Age of Astrology
During the Islamic Golden Age, which spanned from the 8th to the 14th centuries, scholars in the Islamic world made many significant contributions to the fields of astronomy and astrology. Islamic scholars were particularly interested in studying the movement of celestial bodies and their influence on earthly events, and many important advancements in these fields were made during this time.
One of the most notable Islamic scholars of this period was Abu Ma’shar al-Balkhi, who is often referred to as “the prince of astrologers.” Abu Ma’shar made many significant contributions to the field, including the development of techniques for calculating the positions of planets and the use of solar and lunar eclipses to predict events. He also wrote several influential books on astrology; including “The Abbreviation of the Introduction to Astrology“, “The Great Introduction to Astrology“, “The Book of Nativities“, and “On Historical Astrology“; and was widely respected in the Islamic world for his expertise in the field. Another of the most important contributions was made by Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi, a Persian scholar who is credited with inventing the first mechanical astrolabe in the early 9th century CE. The astrolabe became a popular tool for astronomical observations and calculations throughout the Islamic world, and its use eventually spread to Europe during the Middle Ages.
Nostradamus
Almost everyone has heard of this infamous Astrologer, Nostradamus. He lived in France in the 16th century and is well known for his predictions of future events. He wrote a book called Les Propheties (lay PRO-fay-sees), which contained a series of quatrains that he claimed could be used to predict the future. Nostradamus’s predictions were often vague and cryptic, making them difficult to interpret. However, many people believe that some of his predictions have come true. For example, he is said to have predicted the French Revolution, the rise of Adolf Hitler, and the September 11th terrorist attacks in New York City.
One of Nostradamus’s most famous predictions is his prediction of the Great Fire of London, which occurred in 1666. In his book “Les Propheties,” Nostradamus wrote:
“The blood of the just will be demanded of London, Burnt by the fire in the year 66, The ancient Lady will fall from her high place, Many of the same sect will be killed.”
-Nostradamus
Many people believe that this quatrain predicted the fire which began on September 2, 1666, and destroyed much of the city. Some believe that the “ancient Lady” referred to in the quatrain was a personification of London itself. However, it’s important to note that many of Nostradamus’s predictions are open to interpretation and can be applied to a variety of events. Some skeptics believe that Nostradamus’s predictions are simply the result of coincidence and vague language, rather than any real predictive power…nonetheless his words continue to fascinate the world many years after his death.

The History of Modern Astrology
After the Middle Ages, Astrology continued to evolve and grow, with new contributors and innovations that shaped its development into the modern practice that we know today.
One of the most notable figures in the history of astrology during this time was Johannes Kepler, a German astronomer and mathematician who lived in the 16th and 17th centuries. Kepler is perhaps best known for his Laws of Planetary Motion, which helped to establish a more accurate understanding of how the planets move through the solar system. Kepler was also deeply interested in astrology, and believed that the movements of the planets had a direct influence on human affairs. He developed his own system of astrology, which he called “the science of the aspects of the planets.” This system incorporated many of the traditional techniques of astrology, such as the use of horoscopes and the interpretation of planetary positions, but also included some of Kepler’s own innovative ideas.
The invention of the telescope in the 17th century allowed astronomers to observe the movements and positions of the planets with greater accuracy. This led to more accurate astrological predictions, a better understanding of celestial events, and the discovery of the outer planets leading to the addition of Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto into Astrological charts.
In the centuries that followed, astrology continued to evolve and transform, with new systems and approaches emerging in different parts of the world. American astrologer Evangeline Adams, who lived in the early 20th century, was a pioneer in the field of astrology, and was one of the first astrologers to gain widespread recognition and respect in the United States. She wrote several books on astrology such as: “Astrology: Your Place Among the Stars“, “The Bowl of Heaven“, and “Astrology for Everyone“; and gave lectures on the subject, helping to popularize the art and make it more accessible to a wider audience.
In the 20th century, the development of computers and sophisticated software made it possible to create complex astrological charts and calculations quickly and accurately. Astrologers could now input birth data into a program, and within seconds, have a detailed birth chart with planetary positions, aspects, and other key astrological factors. The invention of the internet also made it easier for astrologers to connect with clients from all over the world and offer their services online. Making it easier to access astrological information and resources from anywhere in the world.
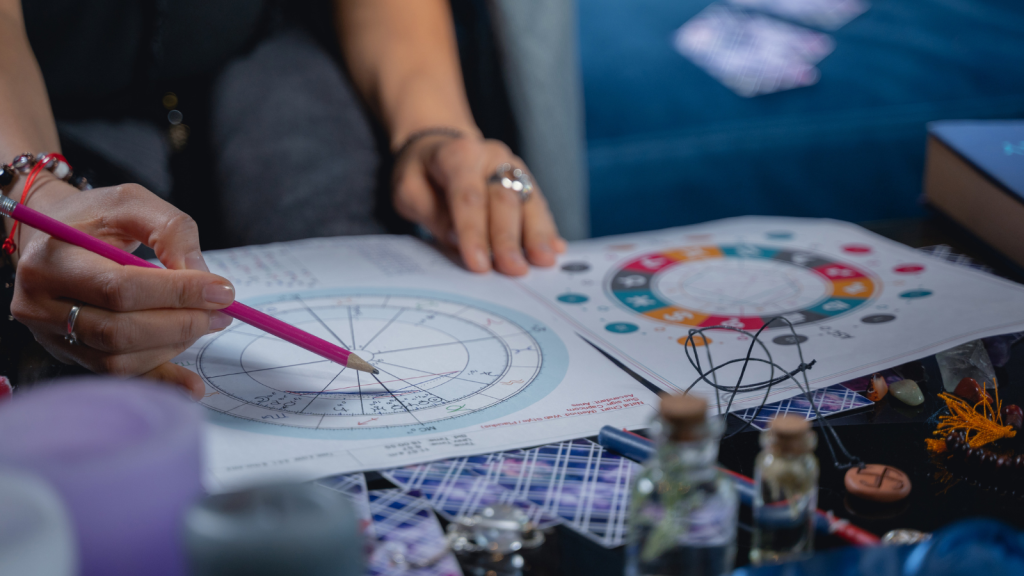

Astrology Today
Astrology has come a long way since its origins in ancient civilizations. Today, it is widely recognized as a tool for self-discovery and personal growth, as well as a means of understanding and predicting world events. Although some may dismiss astrology as mere superstition, its enduring popularity suggests that many people find value in its insights and guidance.
Despite the evolution of technology and the passage of time, astrology continues to be a fascinating and dynamic field. Whether you’re seeking to understand your own inner workings or make sense of the world around you, astrology offers a unique perspective and a powerful tool for exploration.
If you’re interested in learning more about astrology, there are many resources available online and in books. Consider consulting with a professional astrologer to get a personalized reading based on your birth chart. You can also explore the different types of astrology and find one that resonates with you. Keep an open mind and remember that astrology can be a valuable tool for self-discovery and personal growth. So why not take a closer look at the stars and see what they have to tell you?

One of my fabulous friends, (and fellow co-host of the Celestial Café Podcast!) Doogsley over at Faezie.love, is an incredible astrologist and intuitive who loves to dive in to other’s charts and wax poetic about how the stars reflect upon your personality & soul. I’ve personally received several readings from Doogs and I can attest that they are always full of superb insight (and they are just SO MUCH FUN).
Pin it for Later

Sources
“Astrology.” Encyclopedia Britannica
“Did You Know? The Influence of Astrology on the Science of Astronomy along the Silk Roads” UNESCO
“Astrology: Finding Meaning in the Stars” California State University
“Nostradamus.” Encyclopedia Britannica
The Great Introduction to Astrology by Abū Maʿšar
Islamic Astronomy and Geography by David A. King